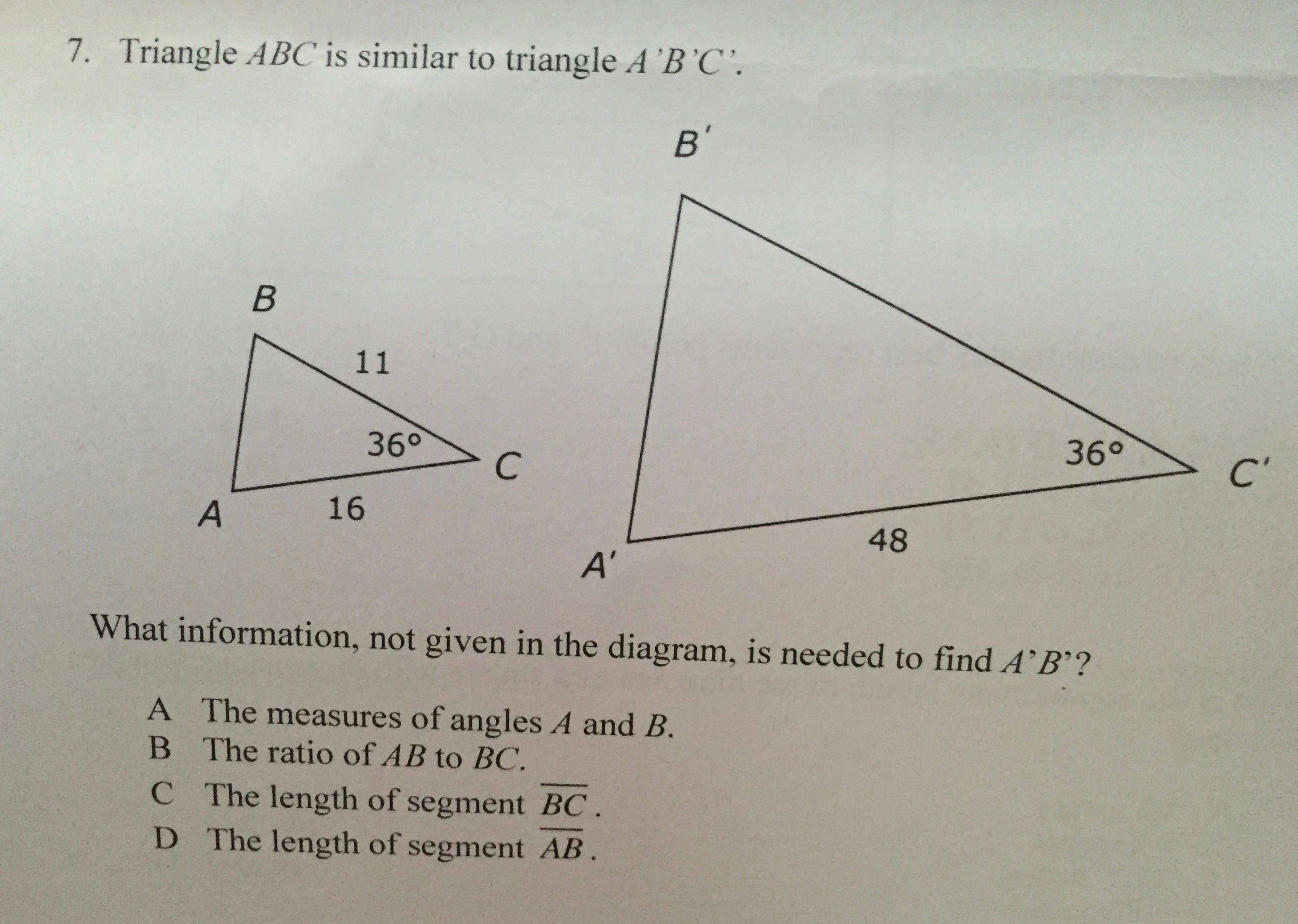
Solved Triangle ABC is similar to triangle A' B' C'. What
Calculator Use A right triangle is a special case of a triangle where 1 angle is equal to 90 degrees. In the case of a right triangle a 2 + b 2 = c 2. This formula is known as the Pythagorean Theorem. In our calculations for a right triangle we only consider 2 known sides to calculate the other 7 unknowns.
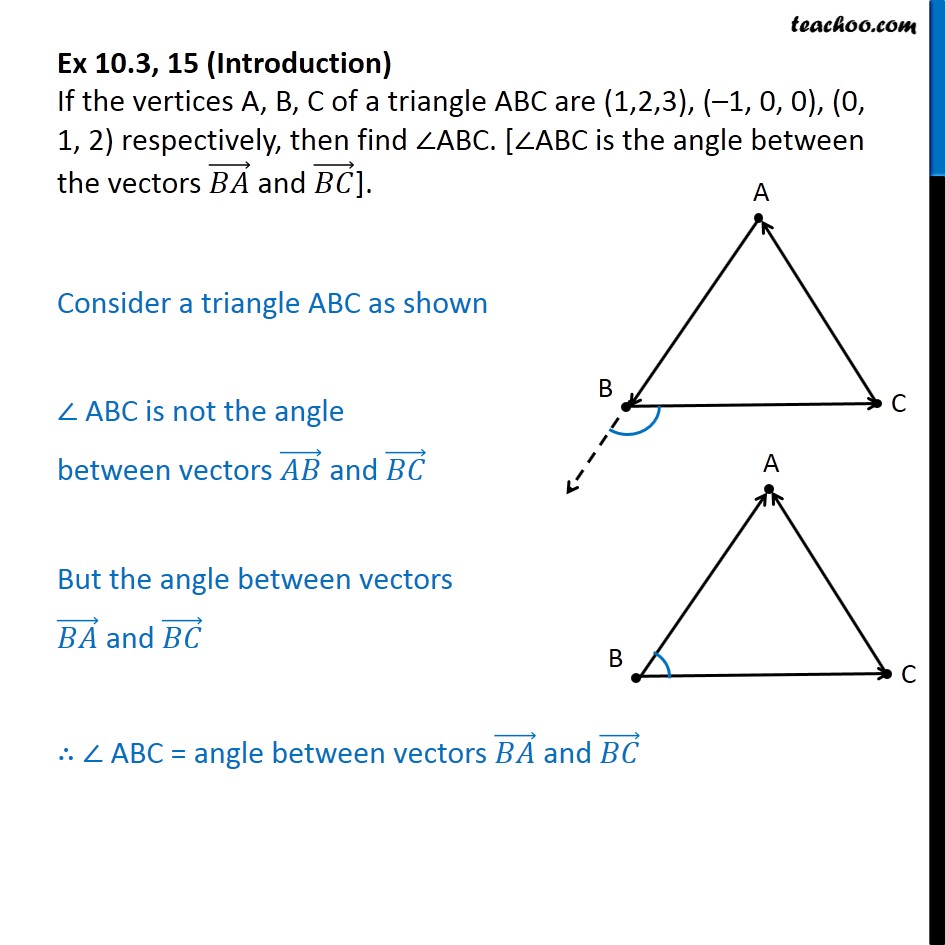
Ex 10.3, 15 If vertices A, B, C of triangle ABC are (1, 2, 3)
the third side of a triangle when we know two sides and the angle between them (like the example above) the angles of a triangle when we know all three sides (as in the following. = a 2 + b 2 − c 2 2ab. cos(A) = b 2 + c 2 − a 2 2bc. cos(B) = c 2 + a 2 − b 2 2ca. Example: Find Angle "C" Using The Law of Cosines (angle version) In this.
[Solved] Solve the triangle B=___° b=____ c=____. C 730 a = 10 490 A B C Course Hero
Naming angles and vertices Referencing the above triangles, an interior angle is formed at each vertex of a triangle. These angles share the same name as their vertices. Thus, the three interior angles for ABC above are A, B, and C. Triangle sides, angles, and congruence

A triangle ABC with vertices A( 1,0), B( 2,3/4), and C( 1,2) has its orthocentre H . Then
Step 1: Enter the values of any two angles and any one side of a triangle below which you want to solve for remaining angle and sides. Triangle calculator finds the values of remaining sides and angles by using Sine Law. Sine law states that a sinA = b sinB = c sinC a sin A = b sin B = c sin C Cosine law states that-
Can an equilateral triangle also be isosceles? Socratic
The Law of Sines. The Law of Sines (or Sine Rule) is very useful for solving triangles: a sin A = b sin B = c sin C. It works for any triangle: a, b and c are sides. A, B and C are angles. (Side a faces angle A, side b faces angle B and. side c faces angle C).
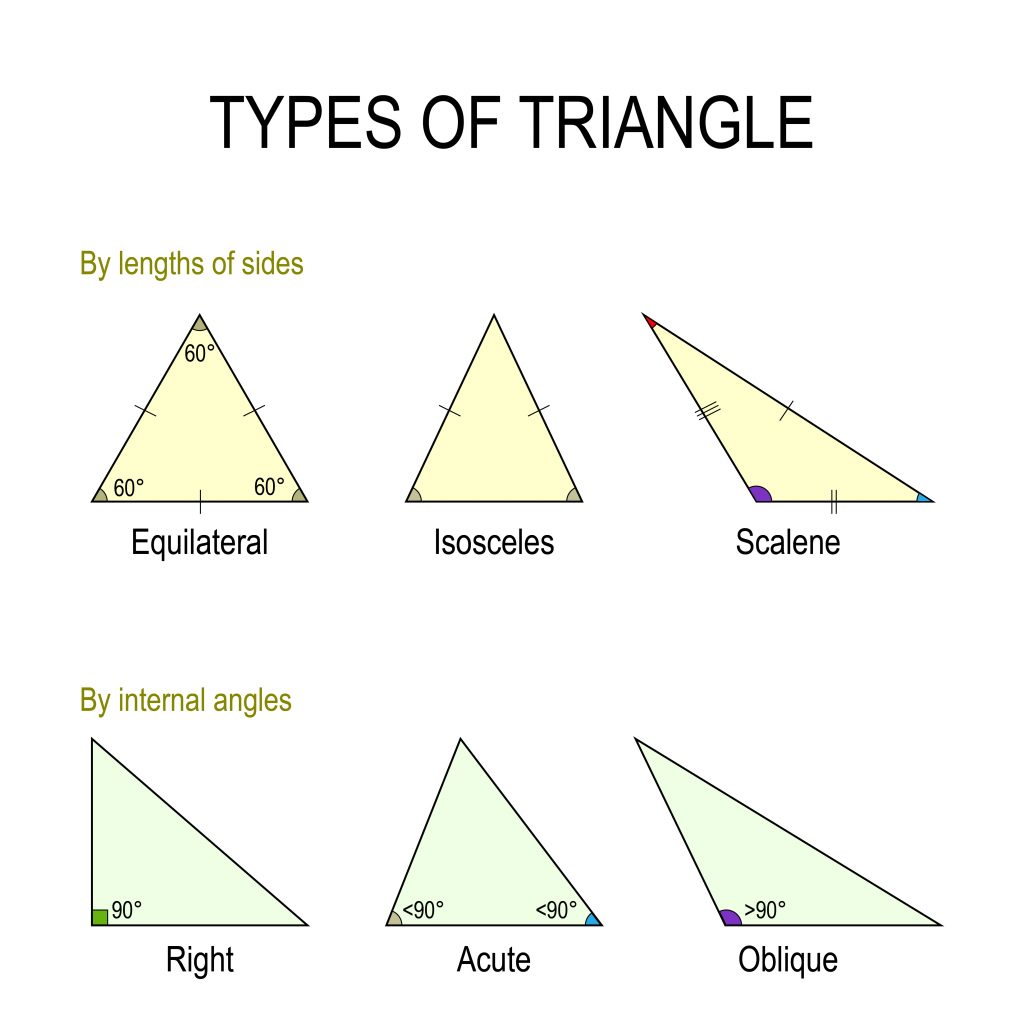
Types & Formulas [Video & Practice] 04/2023
C M E ― Why are these words important? We're about to learn the trigonometric functions—sine, cosine, and tangent—which are defined using the words hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent.

Ex 11.2, 6 Let ABC be a right triangle AB = 6 cm, BC = 8 cm, B = 90
C B A We are given the measure of angle ∠ B and the length of the hypotenuse , and we are asked to find the side opposite to ∠ B . The trigonometric ratio that contains both of those sides is the sine: sin ( ∠ B) = A C A B sin ( 40 ∘) = A C 7 ∠ B = 40 ∘, A B = 7 7 ⋅ sin ( 40 ∘) = A C Now we evaluate using the calculator and round:

Triangle A B C. Angle C is 90 degrees. Hypotenuse A B is 13, adjacent B C is 5, opposite A C is
Triangle A″B″C″ is formed by a reflection over x = −3 and dilation by a scale factor of 3 from the origin. Which equation shows the correct relationship between ΔABC and ΔA″B″C′? Line segment AB/ Line segment A"B" = 1/3. Square T was translated by the rule (x + 2, y + 2) and then dilated from the origin by a scale factor of 3 to.

geometry In the triangle ABC, D and E are points of trisection of segment AB; F is the
Angle bisector theorem Solve triangles: angle bisector theorem Google Classroom You might need: Calculator ∠ D A C = ∠ B A D . What is the length of C D ― ? Round to one decimal place. A D B θ 8.1 2.8 C θ ? 5.9 Show Calculator Stuck? Review related articles/videos or use a hint. Report a problem Do 4 problems

Question Video Finding the Measure of an Angle in a Triangle Using the Relations between the
A=25 C=80 b=22 A=35 C=26 a=10 a=3 C=90 c=5. how to enter right-angled triangle. a=3 β=25 γ=45. triangle calc if we know the side and two angles. a=3 β=25 T=12. triangle calc, if know side, angle, and area of a triangle. T=2.5 c=2 b=4. find side a if we know sides b, c, and the area of triangle T.

A triangle has vertices at B(3,0), C(2, 1), D(1,2). Which transformation would produce an
Given two sides If you know two other sides of the right triangle, it's the easiest option; all you need to do is apply the Pythagorean theorem: a² + b² = c² If leg a is the missing side, then transform the equation to the form where a is on one side and take a square root: a = √ (c² - b²) If leg b is unknown, then: b = √ (c² - a²)

How To Calculate Area Of Triangle With Angle Haiper
Angles Add to 180°: A + B + C = 180°. When you know two angles you can find the third. 2. Law of Sines (the Sine Rule): a sin (A) = b sin (B) = c sin (C) When there is an angle opposite a side, this equation comes to the rescue. Note: angle A is opposite side a, B is opposite b, and C is opposite c. 3.
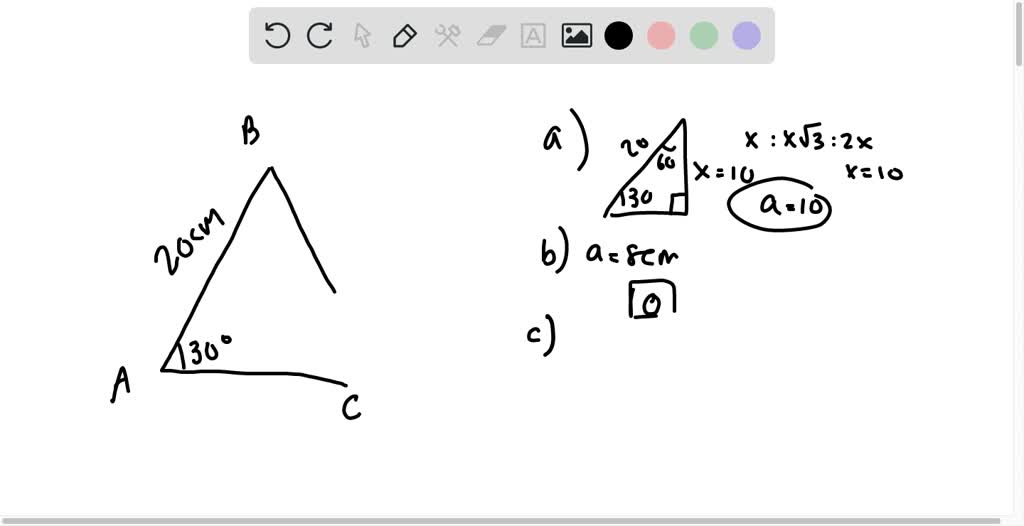
SOLVEDAnswer each question and justify your response using a diagram, but do not solve. Given A
The perimeter of a triangle is equal to the sum of all the sides of the triangle, and the formula is expressed as, Perimeter of a triangle formula, P = (a + b + c), where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are the three sides of the triangle. The equilateral triangle formula for perimeter is, Perimeter of equilateral triangle = (a +a + a) = 3a.

Which of the following is an obtuse triangle? A. Triangle B B. Triangle A C. Triangle D D
In triangle ABC, ∠ C = 90 ∘. If inradius = r and circumradius = R, then find 2(r + R)?(a,b,c are the sides of the triangle opposite to angles A,B and C respectively) View Solution
Triangles A, B and C are shown on the grid. a Describe fully the single transformation that maps
Perimeter of Triangle formula = a + b + c Area of a Triangle
"Triangle B, No. 1" by Walter Stomps, Jr Caza Sikes Art Fine Art Appraisers
For similar triangles A B C and X Y Z shown below: X Y = k ( A B) Y Z = k ( B C) X Z = k ( A C) X Y A B = Y Z B C = X Z A C = k. A B C X Y Z. To calculate a missing side length, we: Write a proportional relationship using two pairs of corresponding sides. Plug in known side lengths. We need to know 3.